Cortrosyn: Package Insert / Prescribing Info
Package insert / product label
Generic name: cosyntropin
Dosage form: injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution
Drug class: Corticotropin
J Code (medical billing code): J0834 (Per 0.25 mg, injection)
Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Jan 16, 2024.
On This Page
Highlights of Prescribing Information
CORTROSYN (cosyntropin) for injection, for intravenous or intramuscular use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2008
Indications and Usage for Cortrosyn
CORTROSYN is an adrenocorticotropin hormone indicated, in combination with other diagnostic tests, for use as a diagnostic agent in the screening of adrenocortical insufficiency in adults and pediatric patients. (1)
Cortrosyn Dosage and Administration
- In general, stop glucocorticoids and spironolactone on the day of CORTROSYN testing. For long-acting glucocorticoids, stop for a longer period before CORTROSYN testing. (2.1)
- For adults, the recommended dose is 0.25 mg to be administered by intravenous or intramuscular injection. (2.2)
- For pediatric patients, the recommended dose to be administered by intravenous or intramuscular injection is (2.3):
o 0.125 mg for patients birth to less than 2 years of age
o 0.25 mg for patients 2 to 17 years of age (2)
- Obtain blood samples for serum cortisol level at baseline and exactly 30 and 60 minutes after CORTROSYN administration. (2.5)
- See Full Prescribing Information for reconstitution and interpretation of cortisol levels information. (2.4, 2.6)
Dosage Forms and Strengths
- For injection: 0.25 mg of cosyntropin as a lyophilized powder in single-dose vial for reconstitution (3)
Contraindications
- CORTROSYN is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to cosyntropin or to any excipients of CORTROSYN. Reactions have included anaphylaxis. (4, 5.1)
Warnings and Precautions
• Hypersensitivity: reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported. Monitor patients for hypersensitivity reactions and treat as needed. (5.1)
• Diagnostic Inaccuracies: Cortisol levels and subsequent diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency following CORTROSYN administration may be inaccurate if patients are on certain medications because of their effect on cortisol or cortisol binding globulin levels. Any condition that elevates or lowers cortisol binding globulin levels may increase or decrease plasma total cortisol levels, respectively. (2.1, 5.2, 7) (5)
Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Drug Interactions
- Drug effects on plasma cortisol levels:
o Accuracy of the test results can be affected by concomitant medications.
o Glucocorticoids and spironolactone: May falsely elevate plasma cortisol levels. Stop these drugs on day of CORTROSYN testing. Long-acting glucocorticoids may need to be stopped for a longer period before CORTROSYN testing. (7)
o Estrogen: May elevate plasma total cortisol levels. Stop estrogen containing drugs 4 to 6 weeks before CORTROSYN testing. (7) (7)
Revised: 12/2024
Full Prescribing Information
1. Indications and Usage for Cortrosyn
CORTROSYN is indicated, in combination with other diagnostic tests, for use as a diagnostic agent in the screening of adrenocortical insufficiency in adults and pediatric patients.
2. Cortrosyn Dosage and Administration
2.1 Important Information Before Conducting CORTROSYN TESTING
- In general, stop glucocorticoids and spironolactone on the day of CORTROSYN testing. However, long-acting glucocorticoids may need to be stopped for a longer period before CORTROSYN testing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7)].
- Stop estrogen-containing drugs four to six weeks before CORTROSYN testing [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7)].
2.2 Recommended Dose for Adults
- The recommended dose of CORTROSYN in adults is 0.25 mg to be administered by intravenous or intramuscular injection.
2.3 Recommended Dose for Pediatric Patients
- The recommended dose of CORTROSYN in pediatric patients, aged birth to 17 years, to be administered by intravenous or intramuscular injection is presented in Table 1.
| Age | Recommended Dose | Volume of Reconstituted Solution |
| Birth to less than 2 years | 0.125 mg | 0.5 mL |
| 2 to 17 years | 0.25 mg | 1 mL |
2.4 Reconstitution Instructions
- Aseptically reconstitute the lyophilized powder in the vial using 1 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP and gently swirl.
- After reconstitution, the final concentration of CORTROSYN reconstituted solution is 0.25 mg/mL.
- Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. The reconstituted CORTROSYN solution should be clear and colorless, and free of particulates. If CORTROSYN solution is cloudy or contains particulates, do not administer.
- If the CORTROSYN reconstituted solution is not used immediately, discard the unused CORTROSYN reconstituted solution.
2.5 Administration Information
- CORTROSYN may be administered by intramuscular or intravenous injection.
- Obtain blood sample for baseline serum cortisol. Obtain blood samples again for assessment of cortisol levels exactly 30 minutes and 60 minutes after administration of CORTROSYN.
2.6 Interpretation of Plasma Cortisol Levels After CORTROSYN Injection
- Stimulated plasma cortisol levels of less than 18 mcg/dL at 30- or 60-minutes post CORTROSYN injection are suggestive of adrenocortical insufficiency. Cutoff values for exclusion of adrenocortical insufficiency may vary according to the assay used. Test results can be affected by concomitant medications and certain medical conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
3. Dosage Forms and Strengths
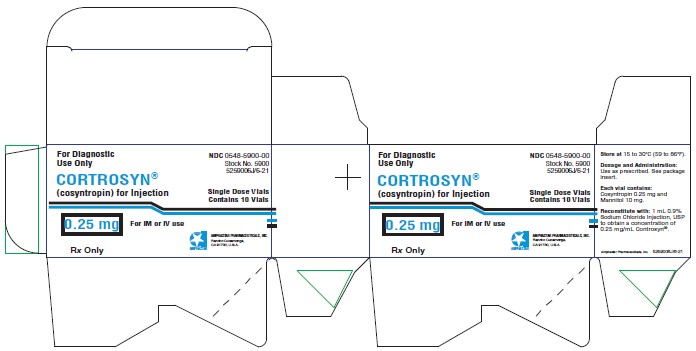
For Injection: 0.25 mg of cosyntropin as a Iyophilized powder in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
4. Contraindications
CORTROSYN is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to cosyntropin or to any excipients of CORTROSYN. Reactions have included anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
5. Warnings and Precautions
5.1 Hypersensitivity to CORTROSYN Injection
CORTROSYN injection hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis have been reported. Monitor patients for hypersensitivity reactions and treat as needed.
5.2 Diagnostic Inaccuracies
Cortisol levels and subsequent diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency following CORTROSYN administration may be inaccurate if patients are on certain medications because of their effect on cortisol or cortisol binding globulin levels.
Glucocorticoids and spironolactone may result in falsely elevated cortisol levels. Stop these drugs on the day of CORTROSYN testing. Long-acting glucocorticoids may need to be stopped for a longer period before CORTROSYN testing [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Estrogen-containing drugs increase cortisol binding globulin levels which can increase plasma total cortisol levels. To obtain accurate plasma total cortisol levels, stop estrogen containing drugs four to six weeks before CORTROSYN testing to allow cortisol binding globulin levels to return to levels within the reference range [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Drug Interactions (7)]. Alternatively, concomitant measurement of cortisol binding globulin at the time of testing can be done; if cortisol binding globulin levels are elevated, plasma total cortisol levels are considered inaccurate.
Any condition that elevates or lowers cortisol binding globulin levels may increase or decrease plasma total cortisol levels, respectively. Cortisol binding globulin levels can be low in cirrhosis or nephrotic syndrome. Measure cortisol binding globulin levels as necessary to ensure accuracy of interpretation of plasma total cortisol levels.
6. Adverse Reactions/Side Effects
Because adverse reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of CORTROSYN:
- anaphylactic reaction
- bradycardia
- tachycardia
- hypertension
- peripheral edema
- rash
7. Drug Interactions
7.1 Drug Effects on Plasma Cortisol Levels
- Accuracy of the test results can be affected by concomitant medications. Plasma cortisol levels and subsequent diagnosis of adrenocortical insufficiency following CORTROSYN administration may be inaccurate if patients are on certain medications because of their effect on cortisol or cortisol binding globulin levels [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Glucocorticoids and spironolactone: May falsely elevate plasma cortisol levels. Stop these drugs on the day of CORTROSYN testing. Long-acting glucocorticoids may need to be stopped for a longer period before CORTROSYN testing.
- Estrogen: May elevate plasma total cortisol levels. Stop estrogen containing drugs 4 to 6 weeks before CORTROSYN testing to allow cortisol binding globulin levels to return to levels within the reference range. Alternatively, concomitant measurement of cortisol binding globulin at the time of testing can be done; if cortisol binding globulin levels are elevated, plasma total cortisol levels are considered inaccurate.
8. Use In Specific Populations
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Available data from case reports over decades of use with cosyntropin during pregnancy have not identified an increased risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Unidentified adrenal insufficiency can result in adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Clinical Considerations).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Unidentified adrenal insufficiency during pregnancy can result in maternal and/or fetal death; therefore, the diagnosis of suspected adrenal insufficiency during pregnancy should not be delayed.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of cosyntropin in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for CORTROSYN and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from CORTROSYN or from the underlying maternal condition.
11. Cortrosyn Description
Cosyntropin is an adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). Cosyntropin is synthetic beta 1 - 24 corticotropin, a synthetic subunit of ACTH. It is an open chain polypeptide containing, the first 24 of the 39 amino acids of natural ACTH in sequence from N terminal. The sequence of amino acids in the 1 - 24 compound is as follows:

The empirical formula is C136H210N40O31S with a molecular weight of 2934 g/mol.
CORTROSYN (cosyntropin) for Injection is a sterile Iyophilized powder in single-dose vials containing 0.25 mg of cosyntropin and 10 mg of mannitol. Sodium Hydroxide and Glacial acetic acid may be used to adjust pH.
12. Cortrosyn - Clinical Pharmacology
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Cosyntropin exhibits the full corticosteroidogenic activity of natural ACTH. Various studies have shown that the biologic activity of ACTH resides in the N-terminal portion of the molecule and that the 1-20 amino acid residue is the minimal sequence retaining full activity. Partial or complete loss of activity is noted with progressive shortening of the chain beyond 20 amino acid residues. For example, the decrement from 20 to 19 results in a 70% loss of potency.
The pharmacologic profile of CORTROSYN is similar to that of purified natural ACTH. It has been established that 0.25 mg of CORTROSYN will stimulate the adrenal cortex maximally and to the same extent as 25 units of natural ACTH. This dose of CORTROSYN will produce maximal secretion of 17-OH corticosteroids, 17-ketosteroids and/or 17-ketogenic steroids.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Animal, human and synthetic ACTH (1-39) which all contain 39 amino acids exhibit similar immunologic activity. This activity resides in the C-terminal portion of the molecule and the 22-39 amino acid residues exhibit the greatest degree of antigenicity. In contrast, synthetic polypeptides containing 1-19 or fewer amino acids have no detectable immunologic activity. Those containing 1-26, 1-24 or 1-23 amino acids have very little immunologic although full biologic activity. This property of CORTROSYN assumes added importance in view of the known antigenicity of natural ACTH.
16. How is Cortrosyn supplied
How Supplied
CORTROSYN (cosyntropin) for injection 0.25 mg, in a single-dose vial for reconstitution.
Box contains 10 single-dose vials NDC 0548-5900-00
Storage and Handling
Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
CORTROSYN injection is intended as a single-dose injection and contains no antimicrobial preservative. Any unused portion should be discarded.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis
Inform patients and/or caregivers of the early signs of hypersensitivity reactions including rash, hives, itching, facial swelling, tightness of the chest, and wheezing [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Drug Interference with CORTROSYN Testing
Advise patients and/or caregivers to stop taking glucocorticoids and spironolactone on the day of CORTROSYN testing. However, for patients taking long-acting glucocorticoids, advise them to stop for longer periods before CORTROSYN testing. Advise patients to stop taking estrogen-containing drugs four to six weeks before CORTROSYN testing [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Drug Interactions (7)].
| CORTROSYN
cosyntropin injection, powder, lyophilized, for solution |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (024736733) |
| Establishment | |||
| Name | Address | ID/FEI | Business Operations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | 024736733 | analysis(0548-5900) , manufacture(0548-5900) | |
More about Cortrosyn (cosyntropin)
- Check interactions
- Compare alternatives
- Pricing & coupons
- Side effects
- Dosage information
- During pregnancy
- Generic availability
- Drug class: corticotropin
- En español